Pile Foundations
Pile foundations are the part of a structure used to carry and transfer the load of the structure to the bearing ground located at some depth below ground surface. The main components of the foundation are the pile cap and the piles. Piles are long and slender members which transfer the load to deeper soil or rock of high bearing capacity avoiding shallow soil of low bearing capacity The main types of materials used for piles are Wood, steel and concrete. Piles made from these materials are driven, drilled or jacked into the ground and connected to pile caps. Depending upon type of soil, pile material and load transmitting characteristic piles are classified accordingly.
Classification of piles
Classification of Pile with respect to Load Transmission and Functional Behaviour.
- End bearing piles (point bearing piles)
- Friction piles (cohesion piles )
- Combination of friction and cohesion piles
Classification of Pile with respect to type of material. Timber
- Concrete
- Steel
- Composite Piles
Classification of Pile with respect to effect on the soil.
- Driven Pile ( Displacement pile)
- Bored Pile ( Non Displacement pile)
Classification of Pile with respect to Shore.
- On Shore ( Land Pile)
- Off Shore (Marine Pile)
Marine Piling
Marine piling work differs from land piling work in many respects.
- Distance from land
- Depth of water
- Hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy
- Underwater currents
- Wave and swells
- Tidal variation
- Wind and storm
- Cyclone
- Existing navigation and possibility of diversion etc.
- Marine Piling
Offshore Piling Works:
This kind of piling works are mostly carried out in construction of various marine structures like jetties, harbours, ports, wharfs and bridges on river/sea that are away from land.
Marine Piles can be installed by
- Tripod Rig.
- Rotary Rig ( Wirth Rig or Ordinary Crawler Mounted Hydraulic Rig)

Tripod Rig
Marine Piling
Different methods commonly used for advancing the bore holes.
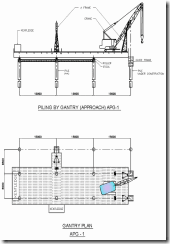
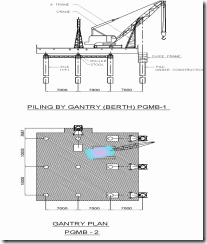
- End on Piling Gantry ( Temporary movable gantry )
- Self elevated Platform ( Jack-up platform )
- Temporary fixed platform supported on temporary/ permanent piles.

Jack Up Platform with Bailer & Chisel

Temporary Movable Gantry with Bailer & Chisel

Temporary Movable Gantry with Bailer & Chisel

 GANTRY
GANTRY 
Fixed Platform with Bailer & Chisel

Piling by Wirth Rig
• Fabrication
A. Fabrication of Gantry
B. Fabrication of Bracings
C. Fabrication of casing
D. Fabrication of Reinforcement
•
Transportation of Liner casing and Reinforcement cage.
•
Driving of Temporary Piles
•
Bracing of Temporary Piles
•
Placing of Wheel Chair and Wheel Blocks.
End on Piling Gantry
SEQUENCE OF WORK
• Erection of Gantry and Components with equipments.
• Guide Frame Fixing.
• Installation of Casing.
• Pile Boring and Chiseling.
• Lowering of Reinforcement cage.
• Tremie Lowering and Flushing.
• Concreting of Pile.
• Shifting of Gantry.
• Recording of Data.
End on Piling Gantry
SEQUENCE OF WORK
• Floating barge/ Pontoon ( 60t -200t)
• Crane (capacity 40t-80t)
• Vibro-Hammer (Static line pull 360 kN/400 kN)
• Tug/Boat (500HP/160H.P.)
• Material barge (100 ton capacity)
• Gantry platform (complete structural steel assembly).
• 5 t Capacity D/D winch with 6YDA Engine/ 3.5 t Capacity D/D winch with 4YDA Engine.
End on Piling Gantry
Major Equipments are Required
• Piling booms
• Bailors & chisels
• Flushing system.
• 200mm/250mm inner diameter tremie pipes
• Concrete funnel (capacity 1cum)
• Welding transformer -18 KVA
• 40KVA/75KVA & 125KVA D.G. sets
• Compressor (300 cfm.)
End on Piling Gantry
• Fixed Platform fabricated on land.
• A’ Frame and winch machine mounted.
• If required, counter weight shall be placed.
• Fixed Platform will be placed in position by the help of land based crane.
• Piles required for erection of gantry shall be done by crane barge using Vibro-hammer.
• The crane barge shall be shifted and positioned at an accuracy of half meter.
• The fabricated liners shall be held in position with help of Vibro-hammer & crane mounted on crane barge, which later shall drive the liner in the seabed.
• Balance piles shall be done by gantry platform mounted on wheels.
POSITIONING OF GANTRY / FIXED PLATFORM
20
 GANTRY PILING GANTRY ERECTION
GANTRY PILING GANTRY ERECTION
Fabrication of Bracing



Liner rolling
Welding of Liner plates

Cage being fabricated on elevated platform. Cover blocks tied in position

Spreader Beam

Temporary piles by Vibro with guide frame


Single Layer bracing

Two layer Bracing
Double layer bracing

Pile Bracings
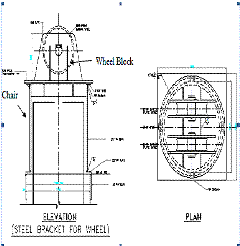

Details of Wheel Bock & Wheel Chair


Typical details of “A” Frame

Guide Frame Fixed at Gantry
“A” Frame Guide Frame SETTING OUT OF PILE POINTS
The pile point shall be marked from approved reference points and bench marks provided by the Client.
Surveyor shall mark the exact pile point with the help of Total Station and accordingly guide frame shall be fixed accurately to Fixed Platform / Gantry.
INSTALLATION OF PERMANENT CASINGS
• M.S casings are fabricated on land.
• Transported to the piling location through material handling barges.
• Lifted by Crane & lowered into the guide frame until it rests on the sea bed.
• Thereafter driven into the seabed by drop hammer up to the refusal, maintaining the verticality & position.
• If found beyond the tolerance then it is retrieved and re-driven in position.
• No boring commences until they are checked to be within tolerance.
• The top and toe level of the installed permanent casing is recorded.

 Liner
DRILLING OF BORE HOLE
Liner
DRILLING OF BORE HOLE
• Bailers and chisel mechanism is used for boring.
• Boring in soil will be done using bailer till the rock level.
• Chisel of appropriate weight is used for boring in hard rock.
• Bailer is used for removing the muck from the pile bore.
• Boring in hard rock is done until the depth in hard rock reaches two times the diameter of pile.
• Throughout boring operations the excavated material is monitored and sampled as far as practical, for any visible changes in material make up.
| Sr. No | Dia. Of Pile in mm | Dia of Chisel in mm | Weight of Chisel in tons | Dia of Bailor in mm | Weight of Bailor in tons |
| 1 | 900 | 825 | Above 2 .0 | 825 | About 1.5 |
| 2 | 1000 | 925 | 2.0- 2.5 | 925 | 1.4-1.7 |
| 3 | 1100 | 1025 | 2.5-2.8 | 1025 | 1.7-1.9 |
| 4 | 1200 | 1125 | 2.8-3.0 | 1125 | 1.9-2.0 |
| 5 | 1300 | 1225 | 3.0- 3.3 | 1225 | 2.0-2.2 |


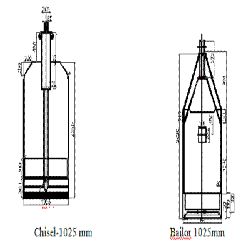
Details of Chisel & Bailor


Boring by bailor
Boring by chisel
REINFORCEMENT CAGE INSTALLATION
• The reinforcement cage is fabricated in the cage fabrication yard.
• Cover blocks of 75mm diameter are fixed at 4 no. per level at 3m vertical intervals throughout the pile length.
• Reinforcement cage are fed to the ‘A’ frame from the barge with the help of crane.
• These cages are lap welded/coupled at site and lowered up to the actual founding level.
• An inspection is carried out as per the check list.


Lowering of reinforcement cage in pile casing
PILE CONCRETING
• Concrete is poured by Tremie Method
• After placing the reinforcement cage, Tremie pipe (200mm dia, 1.5m long) elements are assembled and lowered inside the pile.
• Tremie pipe connected to a hopper is held by ‘A’ frame.
• Borehole is cleaned by air/ water flushing method till clear water is obtained.
• The concreting shall be done by using the crane and bucket arrangement from the transit mixture to pile.
• The concrete shall be poured into the tremie pipe hopper without interruption.
PILE CONCRETING
• The bottom of tremie pipe shall at all be embedded at least 3 m into the concrete as being cast into the pile the tremie segment will be progressively withdrawn during the process of concreting. The window (150 mm X 100 mm) shall be provided at pile cut-off level. As concrete is placed into the pile, a cross check shall be carried out comparing the actual vertical build up of the concrete in the pile, against the theoretical calculated build up concrete for the cast volume of concrete. The contaminated concrete shall be allowed to overflow till the good quality concrete is obtained (By visual inspection).
PILE CONCRETING
• Concrete pour register shall be maintained for all piles.The reinforcement cage is fabricated in the cage fabrication yard.
• Cover blocks of 75mm diameter are fixed at 4 no. per level at 3m vertical intervals throughout the pile length.
• Reinforcement cage are fed to the ‘A’ frame from the barge with the help of crane.
• These cages are lap welded/coupled at site and lowered up to the actual founding level.
• An inspection is carried out as per the check list.


Tremie lowering
 SEQUENCE OF WORK
SEQUENCE OF WORK
Positioning of Jack Up.
• Setting out of Pile Points.
• Installation of Casing.
• Pile Boring and Chiseling.
• Lowering of Reinforcement cage.
• Tremie Lowering and Flushing.
• Concreting of Pile.
• Shifting of Gantry.
• Recording of Data.
Piling By Self Elevated Platform ( Jack-Up)
• Surveyor shall approximately mark the pile location by marker buoy with the help of total station.
• The Jack up platform shall be shifted to the required location/position of the proposed pile location by a tug/ power boat.
• Then the Jack-Up shall be positioned at an accuracy of half meter to the marked location with help of boats/tugs.
• Then the Jack up anchors shall be released from Jack up and Jack up shall be placed in position by tug.
Positioning of Jack Up.
• Once the Jack up anchors are placed, the spuds of the jack-up shall be lowered till the sea bed level. Jack up shall be jacked up to appropriate level usually above the cutoff level of pile
• Survey points shall be marked on the projected guide platform, fixed on to the jack-up platform.
• Piling Boom along with Winch shall be centered & installed on the Jack – up platform.
 Positioning of Jack-Up Platform with help of tug INSTALLATION OF PERMANENT CASINGS
Positioning of Jack-Up Platform with help of tug INSTALLATION OF PERMANENT CASINGS 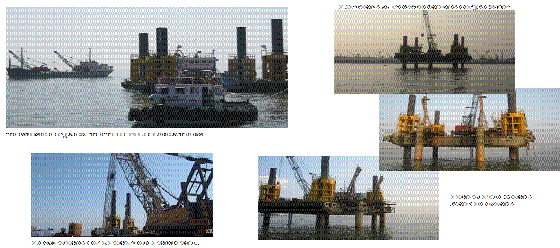 PILING BY JACK-UP
PILING BY JACK-UP



















































